Close
Download
TECHNICAL DATA AND GUIDELINES FOR THE CHOICE
Basic data required
- disturbing frequency: the frequency of the disturbing vibration produced by a on-duty machine. In general, it is obtained by the number of rotations of the engine [Hz=r.p.m./60];
- the load applied to every single vibration-damping element [N];
- the isolation degree required [%];
- the deflection value of the vibration-damping element under a given load [mm];
- the rigidity [N/mm], that is to say the load that applied to the vibration-damping element produces a deflection of 1.0 mm.
How to choose the vibration-damping element
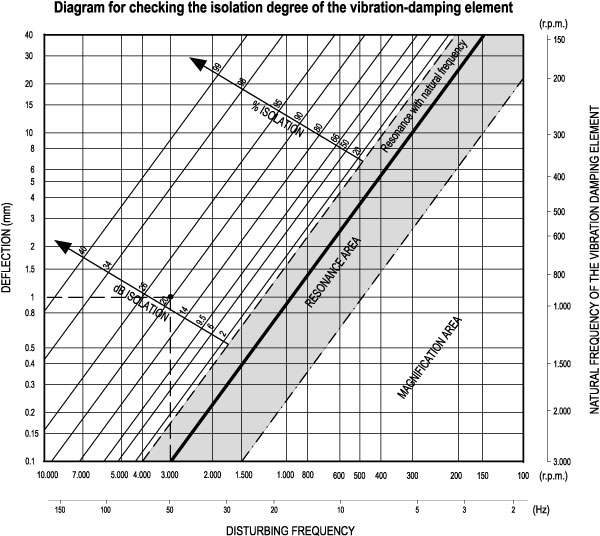
- with reference to the diagram for checking the isolation degree, intersect the disturbing frequency value with the isolation degree required (each isolation degree corresponds to a line in the diagram) and define the deflection [in mm];
- divide the load applied onto the vibration-damping element by the deflection value to obtain the required rigidity of the vibration-damping element;
- compare the rigidity obtained with the rigidity shown in the table and choose the vibration-damping element which presents the nearest value (lower) to the calculated one.
- the rigidity values reported in the table refer to the maximum load values.
- the designer must verify that the article chosen through this selection criterion is suitable for the application required, in any case. For this purpose on request for each article, non-linear graphs of the spread (according to the applied load) are available.
Example
Conditions of use:
- disturbing frequency= 50 Hz (3,000 r.p.m.);
- load applied on each vibration-damping element 120 N;
- 90% isolation required;
- diagram shows that with a 50 Hz disturbing frequency and an isolation degree of 90%, the deflection obtained is 1.0 mm;
- divide the load applied by the deflection obtained to define the rigidity required, which is 120/1.0 = 120 N/mm;
- compare the rigidity value obtained (120 N/mm) with the values reported in the table;
- the values reported in table, for type DVA.1, show that the vibration-damping element which should be used is DVA.1-25-20-M6-18-55.
-
Generals
-
1. Plastic materials
- 1.1 Mechanical strength
- 1.2 Thermal resistance
- 1.3 Strength and surface hardness
- 1.4 Resistance to chemical agents
- 1.5 Resistance to atmospheric agents and uv rays
- 1.6 Flame resistance
- 1.7 Electrical properties
- 1.8 Surface finish and cleanability
- 1.9 Compliance with international standards
- 1.10 Competence of Elesa+Ganter technical department
- 2. Metal materials
- 3. Other materials
- 4. Machining tolerances
- 5. Fixed handles
- 6. Assembly measures
- 7. Special executions
- 8. Colours
- 9. Test values
-
10. Technical tables
- 10.1 Conversion tables
- 10.2 DIN 79 Square holes and shafts
- 10.3 DIN 6885 Keyways
- 10.4 GN 110 and GN 110.1 Transversal holes
- 10.5 DIN 13 ISO Metric threads
- 10.6 DIN 228 Cylindrical GAS-BSP threads
- 10.7 DIN EN ISO 898-1 | DIN EN 20898-2 Strenght values
- 10.8 DIN ISO 286 ISO-Fundamental tolerances
- 10.9 IP Protection Classification
- 10.10.1 PFB | PRB Thread locking with jamming action Polyamide patch coating/ Polyamide complete coating
- 10.10.2 MVK Thread locking gluing Micro encapsulation precote 80 (red)
- 10.11 Stainless Steel characteristics
- 10.12 Surface treatments
- 10.13 Carbon steel, zinc alloys, aluminium, brass characteristics
- 10.14.1 Duroplast, elastomer, technopolymer and rubber characteristics
- 10.14.2 Duroplast, elastomer, technopolymer and rubber characteristics
- 10.14.3 Duroplast, elastomer, technopolymer and rubber characteristics
- 10.15 Load ratings U-Handles
- 10.16 Load ratings metal hinges
- 10.17 Strength of indexing plungers
- 10.18 Assembly sets GN 965 and GN 968
- 11. Vibration-damping elements
-
1. Plastic materials
- Hygienic design
- Operating Elements
- Clamping knobs
- Control elements
- Rotary controls
- Indexing elements
- Joints
- Transmission elements
- Levelling elements
- Hinges
- Latches
- Toggle, power and hook clamps
- Accessories for hydraulic systems
- Tube clamp connectors
- Castors and wheels
- Magnets
- Conveyor components
- Linear slides
- Vibration mounts
- Vacuum components
- Elastomer springs



